With a growing awareness of environmental issues, you may find yourself increasingly concerned about the disproportionate impact of chemical companies like Chemours in Fayetteville. This community faces significant challenges, including increased health risks and compromised local ecosystems due to hazardous waste and pollution. You have the right to understand the serious consequences of industrial activities on your environment and explore potential avenues for change. This post researchs into the specifics of these injustices and highlights efforts to combat them, aiming to empower you with knowledge and awareness.
Understanding Environmental Injustice
Definition and Historical Context
To truly grasp the concept of environmental injustice, you must first acknowledge that it refers to the disproportionate impact of environmental hazards on marginalized communities. This phenomenon is rooted in a historical context where communities of color, low-income families, and indigenous populations have been exploited and disproportionately affected by industrial pollution, toxic waste, and unsound environmental practices. As the landscape of industrial development has evolved, many marginalized communities have found themselves bearing the brunt of toxic exposure, often lacking the resources or political power needed to advocate for their rights and protect their environment.
To understand the present situation in places like Fayetteville, it’s important to look at the history of regulatory enforcement and corporate accountability. The laws that govern environmental protections, such as the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act, were designed to safeguard public health and the environment. However, inconsistencies in enforcement, along with a history of systemic discrimination, have resulted in marginalized communities facing higher rates of pollution and related health issues. By reflecting on this history, you begin to see the complex web of factors that contribute to environmental injustice.
Key Terms and Concepts
One of the fundamental concepts in understanding environmental injustice is the term ‘disproportionate burden.’ This refers to the scenario where vulnerable communities experience a higher level of environmental hazards compared to their more affluent counterparts, often without adequate remediation. Another key term is ‘environmental racism,’ which highlights the systemic policies and practices that intentionally or unintentionally place people of color at greater risk of environmental harm. By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you can better understand the frameworks that contribute to the ongoing challenges faced by affected communities.
But it is not just terminology that you should focus on; you also need to grasp the interconnectedness of these concepts. The systemic disparity in environmental protections illustrates how socio-economic factors, political power dynamics, and historical injustices converge to create environments where certain communities suffer more than others. Understanding these key concepts allows you to discern the patterns of inequality that characterize cases of environmental injustice, such as Chemours’ impact on Fayetteville. By staying informed, you can become an advocate for change, raising awareness on how these issues affect your community and those of others facing similar challenges.
Chemours: Company Overview
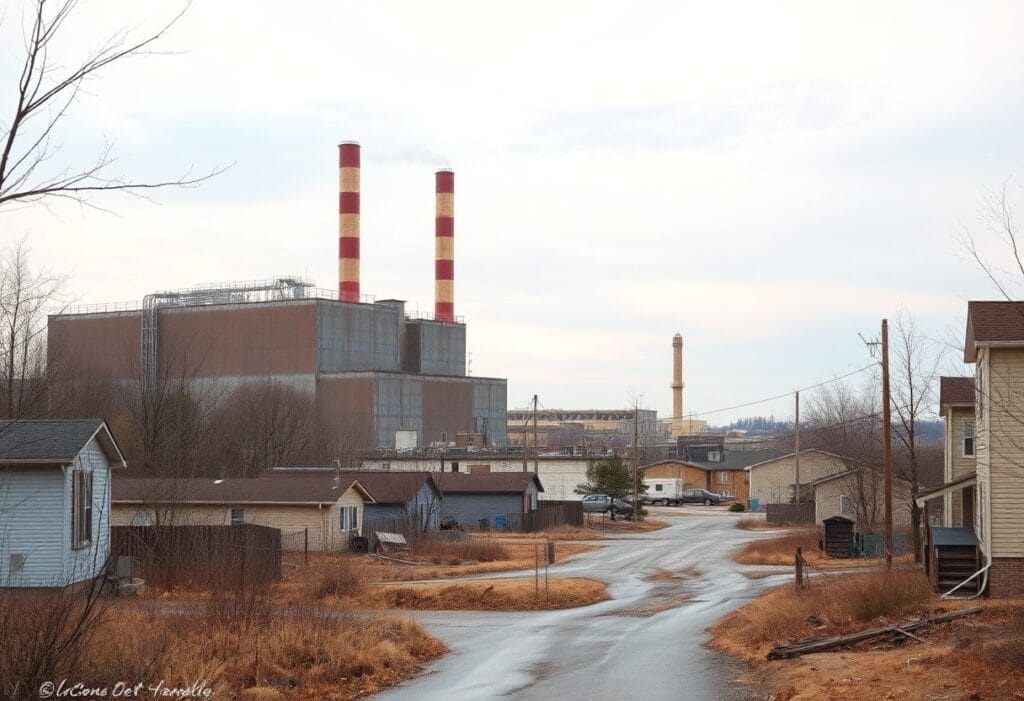
One of the leading chemical companies in the United States, Chemours was spun off from DuPont in 2015. This transition allowed Chemours to specialize in a range of industrial and specialty chemicals, including those used in various manufacturing processes and consumer products. With a significant presence in Fayetteville, North Carolina, the company has made a name for itself by producing advanced materials such as fluoroproducts and chemical solutions, which are imperative in sectors like electronics and coating industries. However, its operations have also raised serious concerns regarding environmental repercussions and public health risks in the surrounding communities.
History and Operations
After its establishment as an independent entity, Chemours focused on enhancing its global footprint while improving its product offerings. You might find it interesting that the Fayetteville Works facility, established in the 1960s, became one of the largest production sites for Chemours and has been integral to its growth strategy. However, as the company expanded its operations, it also attracted scrutiny for its environmental practices, particularly concerning the discharge of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). These compounds have garnered attention for their persistence in the environment and potential risks to human health.
Chemical Processes and Products
To understand Chemours’ impact, it is imperative to research into the specific chemical processes involved in their product manufacturing. The company specializes in producing a variety of fluorochemical offerings, including Teflon and other related coatings. These products have significant utility in the market; however, the processes used to create them often involve synthetic chemicals that can be hazardous to both the environment and public health. The production methods frequently raise alarms due to their connections to pollution and contamination in local water supplies.
And while Chemours does contribute positively through innovative materials that enhance efficiency and durability in products, the usage of harmful chemicals raises alarms. Many of its products release PFAS and other toxic byproducts during manufacturing. Consequently, when discussing Chemours’ role in Fayetteville, it’s imperative to weigh both the economic benefits and the environmental implications, as the latter can have a lasting impact on the health of the communities surrounding their facilities.
Fayetteville: A Case Study
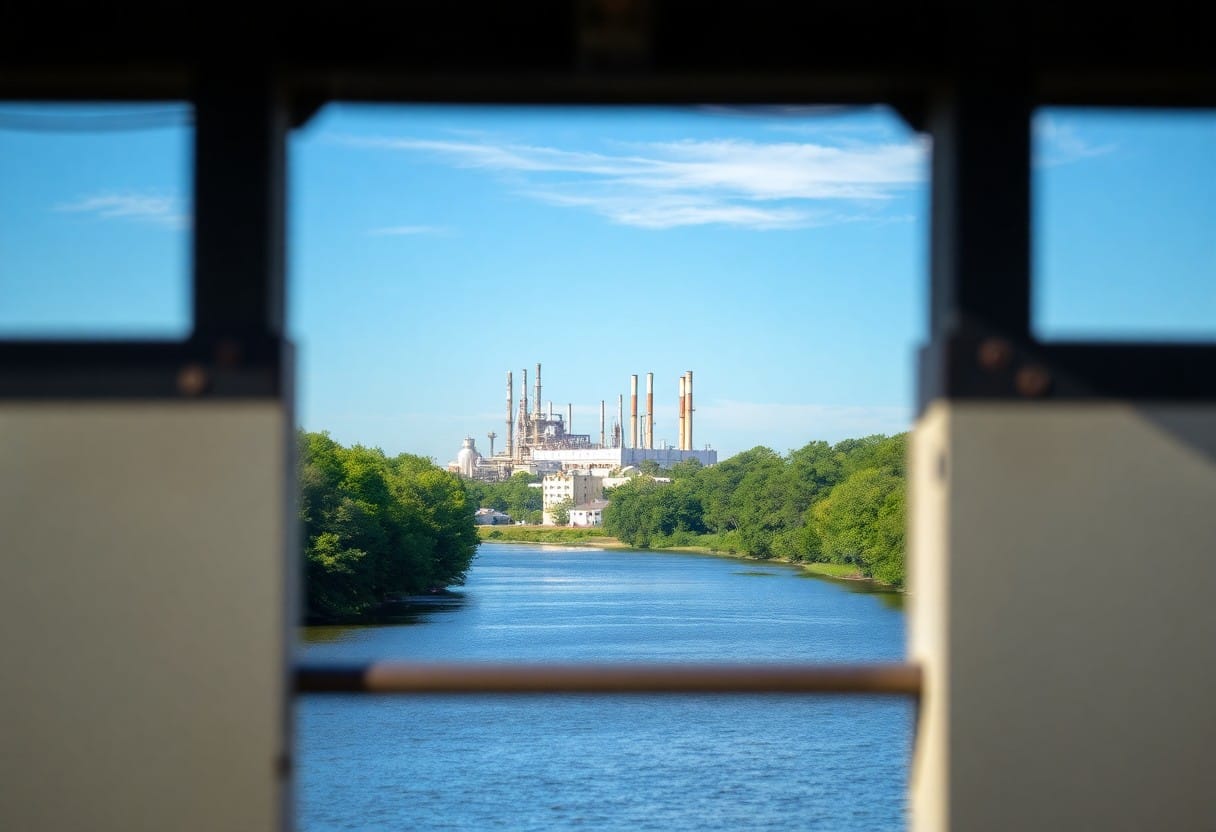
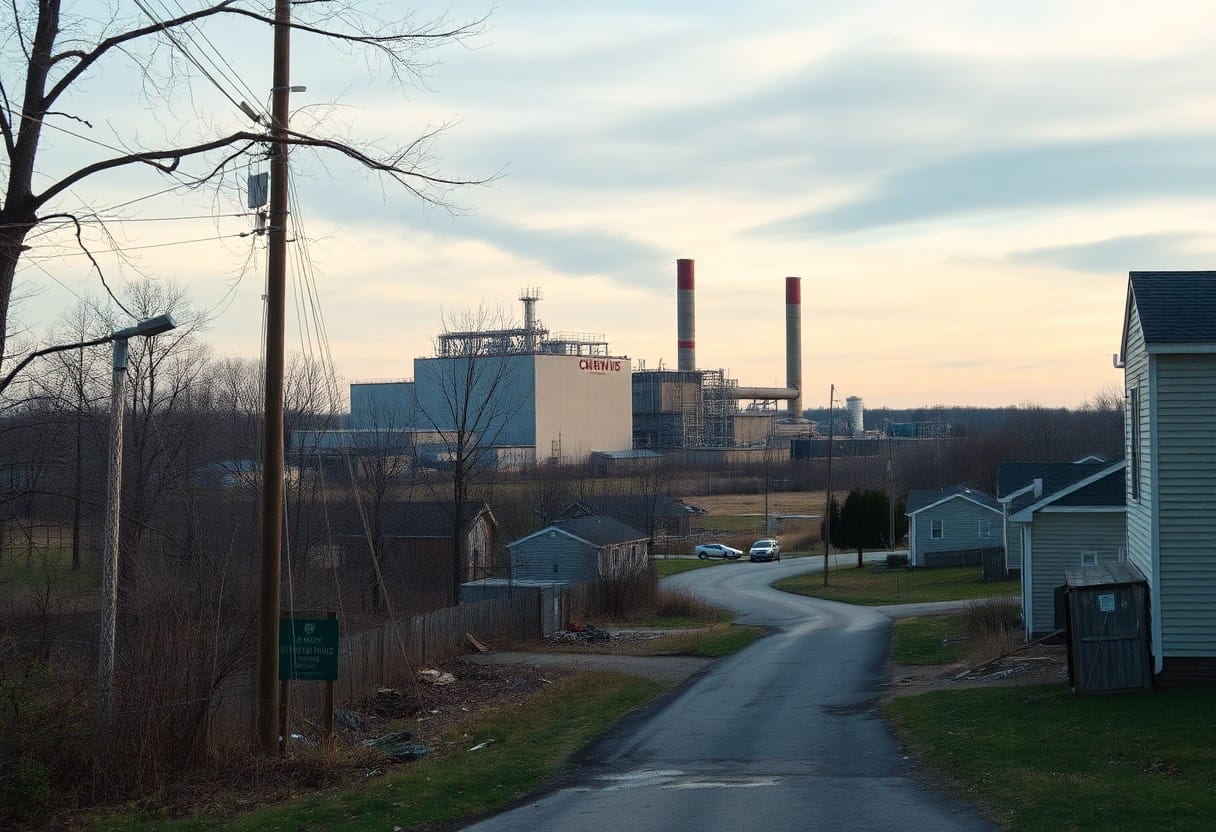
While the state of environmental injustice is pervasive across many regions, Fayetteville presents a particularly alarming example of how industrial practices can have a disproportionate impact on specific communities. The presence of Chemours, a chemical manufacturing company, has raised serious concerns regarding Fighting forever chemicals and their effect on local populations. As you investigate into the specifics of Fayetteville’s challenges, the intersections of race and socioeconomic status will become glaringly evident in understanding the broader issue of environmental injustice within this context.
Community Demographics
Around Fayetteville, the demographic profile reveals significant disparities that highlight the uneven burden of environmental hazards. You will notice that many residents belong to lower-income households, and a substantial portion of the population identifies as people of color. These factors play a pivotal role in determining the health outcomes of communities exposed to pollutants from industry, as individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds often have less access to resources that can mitigate these risks.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Assessment of the environmental effects caused by Chemours reveals a troubling situation for the Fayetteville community. The release of harmful substances, particularly per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), raises serious alarms about water quality and public health. You may find it alarming that studies have shown elevated levels of these chemicals in nearby water sources, posing long-term health risks to residents and wildlife alike.
For instance, the ongoing detection of PFAS in groundwater and surface water has led to *profound concerns regarding the long-term implications on human health*, including potential links to cancer and reproductive issues. The comprehensive nature of the environmental impact assessment focuses not only on immediate risks but also on the cumulative effects that these pollutants can have over time, stressing the need for immediate action and awareness in addressing these environmental disparities in Fayetteville.

Health Implications for Local Residents
Many residents of Fayetteville are deeply concerned about the health implications resulting from Chemours’ operations. The introduction of forever chemicals found disproportionately in poorer, more vulnerable communities has been linked to a variety of health issues. Local water supplies have been contaminated, raising fears and questions about the safety of drinking water and long-term exposure to hazardous substances. The potential for harm varies significantly across socioeconomic lines, whereby residents in marginalized neighborhoods face a greater risk of exposure and, subsequently, adverse health outcomes.
Exposure to Hazardous Chemicals
Residents have expressed worry about their exposure to hazardous chemicals released by Chemours, particularly PFAS (Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), which are notoriously difficult to break down. Many of these chemicals can accumulate in your body over time, leading to severe repercussions for your health. These substances have been found in rivers, groundwater, and even the air around the facility, exposing nearby communities to contaminants that can compromise their overall well-being.
Long-term Health Effects
Any long-term exposure to PFAS and other hazardous chemicals can result in significant health problems, including increased risk of cancer, liver damage, and developmental issues in children. These chemicals have been linked to various endocrine disorders as well, which can disrupt hormone balance and lead to further complications. As a resident of Fayetteville, the implications of ongoing exposure may well endanger not only your health but also the health of future generations.
It is imperative for you to stay informed about the potential health impacts of these hazardous substances. The emerging research surrounding PFAS has highlighted a range of *serious illnesses* linked to long-term exposure, including *thyroid disease, immune system dysfunction*, and *reproductive health issues*. Therefore, understanding these risks and advocating for better regulation and cleanup efforts has never been more important for the health of you and your community.
Regulatory Responses and Legal Actions
Government Intervention
Below, you will find that government intervention has played a significant role in addressing the environmental concerns related to Chemours’ activities in Fayetteville. After community members raised alarms about the hazardous chemical discharges and their impact on public health, various regulatory bodies, including the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), initiated investigations. These investigations have led to increased scrutiny of Chemours’ operations and heightened regulatory measures aimed at reducing pollution levels. This increased oversight not only holds the company accountable but also seeks to protect vulnerable communities that are most affected by these emissions.
Additionally, legislation has surfaced in response to the pervasive issues caused by chemical manufacturing practices. State and local governments have begun to implement stricter regulations regarding waste management and emissions controls, which could eventually lead to better quality of life for residents in affected neighborhoods. These regulatory efforts signal a growing recognition of the need for environmental justice, especially for communities that have historically borne the brunt of industrial pollution without adequate support.
Community Advocacy Efforts
Below, you will learn that community advocacy efforts have emerged as a powerful force in addressing the environmental injustices caused by Chemours. Local organizations and grassroots movements have mobilized to raise awareness about the health risks associated with chemical exposure. By uniting residents, activists have been able to draw attention to the long-standing neglect of federal and state authorities in enforcing environmental regulations. Their efforts have led to more significant public discourse around toxic exposure, compelling policymakers to act to protect residents.
Legal actions undertaken by community groups have resulted in lawsuits against Chemours, demanding accountability for pollution and seeking remedies for affected individuals. These legal avenues not only hold the company responsible but also empower community members, showcasing their resilience and commitment to fighting for a cleaner and safer environment. You might find that the outcomes of these legal battles can set important precedents for other environmental justice cases across the nation, highlighting the power of determined advocacy.
Legal expertise plays an integral role in advocating for change, as community organizations often enlist lawyers specializing in environmental law to navigate complex regulations. These legal teams work to gather evidence, file lawsuits, and support initiatives aimed at enhancing public health protections. As you follow these developments, you’ll see how the combination of legal action and community engagement amplifies the call for equitable treatment and stronger regulations around chemical manufacturing practices.
Solutions and Path Forward
Despite the challenges posed by environmental injustice, particularly in the context of Chemours’ operations in Fayetteville, there are actionable steps you can take to promote a healthier community and advocate for your rights. You can engage with local organizations working on remediation efforts and voice your concerns to policy-makers. Collaboration between residents, environmental advocates, and government agencies is necessary in restoring the community’s well-being and ensuring that the health needs of affected individuals are met. It is also imperative that you stay informed about the developments in cleanup processes and advocate for transparency and accountability from chemical companies operating in your area.
Remediation Strategies
At the heart of addressing environmental injustices in Fayetteville lies the need for effective remediation strategies. You should be aware that these strategies involve comprehensive assessments of contamination levels, subsequent cleanup operations, and ongoing monitoring to ensure the safety of your environment. Advanced technologies can be employed to remediate toxic substances, and these methods must prioritize safe drinking water and soil quality for both current and future generations. Engaging with scientists and environmental specialists can provide you with insights into which methods are most effective and sustainable for your community.
Policy Recommendations
Above all, your voice matters in pushing for policy changes that can help mitigate the impact of Chemours and similar industries. Advocating for stricter regulations on chemical emissions and greater transparency in reporting hazardous waste is vital. You can encourage your local representatives to support legislation aimed at protecting marginalized communities, which often bear the brunt of environmental hazards. Policies should also promote resident involvement in decision-making processes regarding local environmental issues, ensuring that you have a say in matters that directly affect your health.
Considering the systemic nature of environmental injustice, it is necessary that you seek comprehensive policy recommendations that incorporate community input and emphasize corporate accountability. Engaging with local and state governments to establish clear guidelines for monitoring and mitigating contamination will empower you and your neighbors. You should advocate for the establishment of community health assessments and environmental impact statements that take into account the voices and experiences of those most affected. By actively participating in these discussions, you can play a pivotal role in shaping a safer, more equitable environment for yourself and future generations.
Summing up
From above, you can see how the case of Chemours and its impact on the Fayetteville community exemplifies environmental injustice. Residents, particularly in marginalized communities, face disproportionate exposure to harmful pollutants, which can severely affect their health and quality of life. You may wonder how these injustices built into the fabric of environmental policy could persist despite the growing awareness of these issues. This situation calls for your involvement in advocating for equitable policies that protect vulnerable populations from adverse effects caused by industrial activities.
Your understanding of these dynamics is vital for promoting change. By educating yourself and others about the environmental challenges faced by communities like Fayetteville, you can participate in discussions that hold corporations accountable for their actions. Engaging with local advocacy groups or policymakers can amplify your voice and help pave the way for a healthier, more equitable environment for all. It is within your power to contribute to a future where environmental justice is not just a concept, but a reality for every community.